
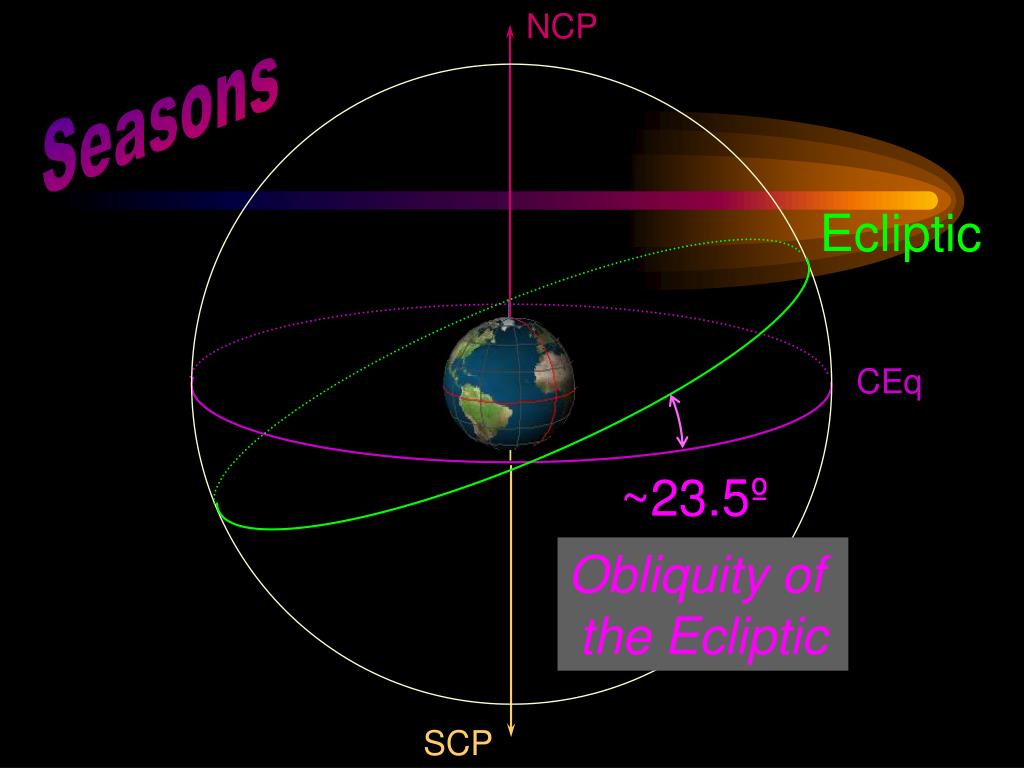
Obliquity of the Ecliptic and Latitudes of Arctic and Antarctic Circles
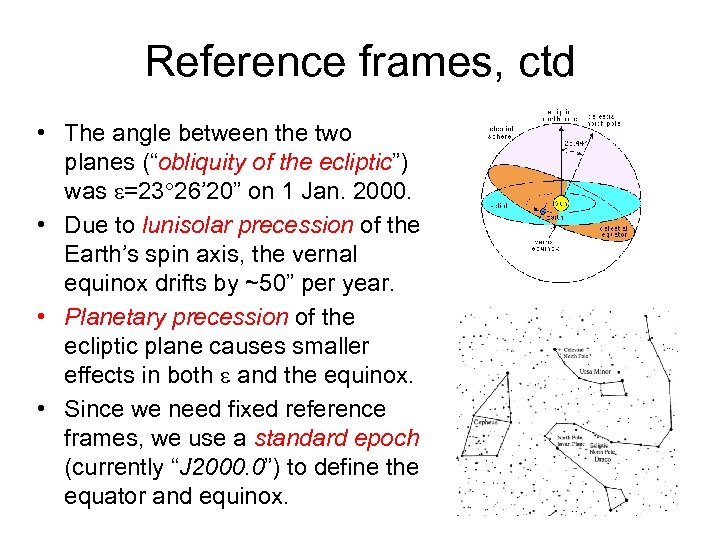
The term used by the astronomers to describe the inclination of the equator of the Earth with respect to the ecliptic of the Earth's rotation axis that is perpendicular to the ecliptic. This term is also known as the obliquity of the ecliptic. Because of the planetary perturbations, it is about 23.4 degrees and it is decreasing per hundred.
PPT The Celestial Sphere PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
4.1 Experiment 1: determination of the obliquity of the ecliptic 4.1.1Description of the experiment To measure the obliquity of the ecliptic the evolution of the declination of the Sun will be monitored over a long period of time (six months). To do this, we'll measure each day the Sun's altitude at solar noon with the help of a gnomon.
Teach Astronomy Navigation
The angle between the Earth's equator and the ecliptic. It is the same as the Earth's axial tilt. The mean obliquity, corresponding to the mean equator, is currently just over 23° 26′, but is decreasing slowly at a rate of 47.5″ per century because of planetary perturbations of the Earth's orbit.

Earth’s Motions Physical Geography
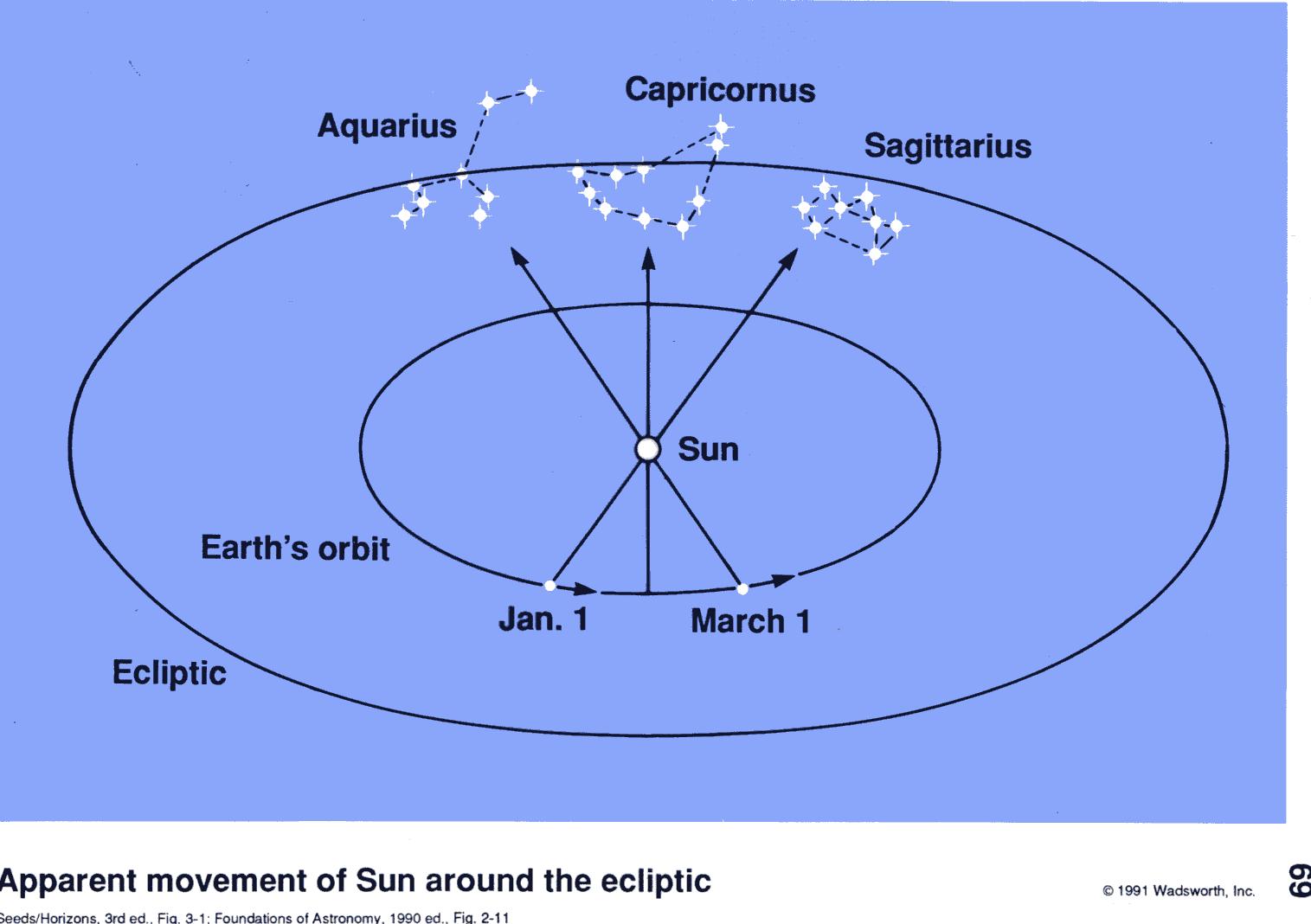
The ecliptic is the Sun 's path through the starry background of the sky. The Moon and planets follow a similar track. The Sun's position relative to the stars is revealed during the darkness of a total solar eclipse.
AST101 Lecture Notes The Reasons for the Seasons
Glossary obliquity Glossary Terms albedo aphelion argument of perihelion ascending node astrometry au (astronomical unit) barycenter declination descending node eccentricity ecliptic plane ephemeris geocentric geodetic GM H (absolute magnitude) heliocentric inclination Lagrange points (L1,L2) Laplace plane LD (lunar distance) line of nodes

Obliquity of the Ecliptic James Nizam
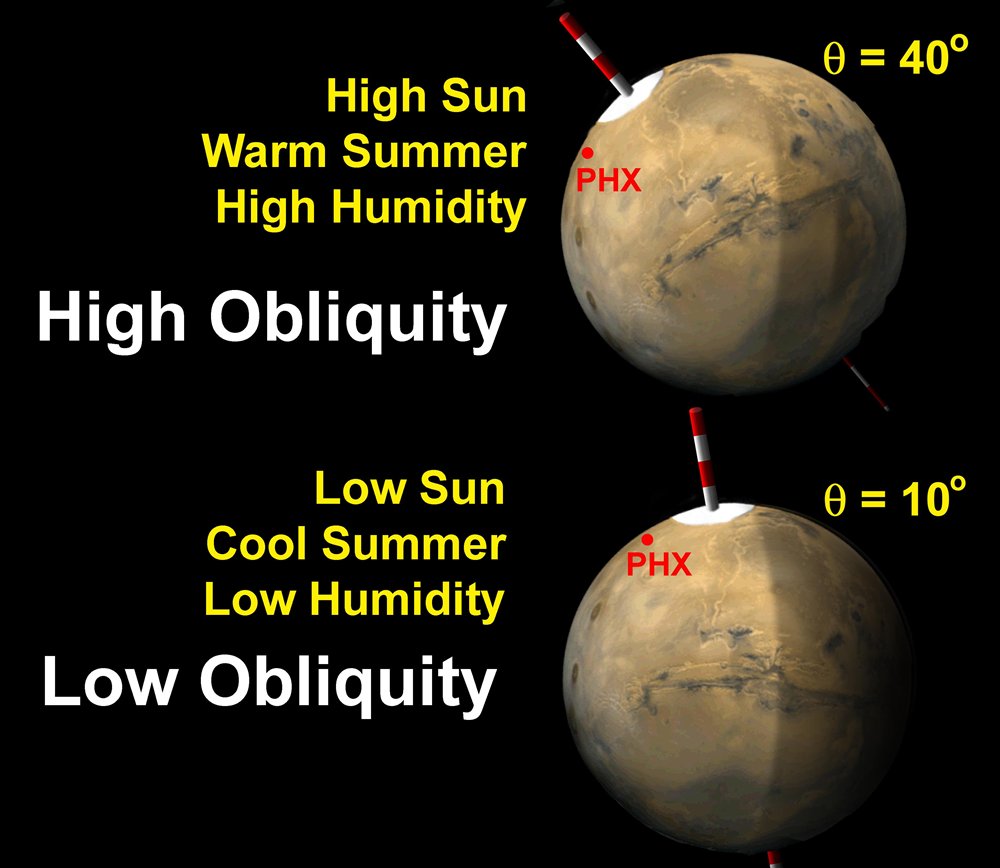
Apsidal precession changes the orientation of Earth's orbit relative to the ecliptic plane.. In addition, it was his belief that obliquity was the most important of the three cycles for climate, because it affects the amount of insolation in Earth's northern high-latitude regions during summer (the relative role of precession versus.
AST101 Lecture Notes The Reasons for the Seasons
In astronomy, an axis refers to the imaginary line that an object, usually a planet, rotates around. Earth's rotational axis is an imaginary straight line that runs through the North and South Pole. In our illustrations, Earth's axis is drawn as a straight red line. Giant Impact Hypothesis

Orientation of the Earth in space the plane defined by the Earth's
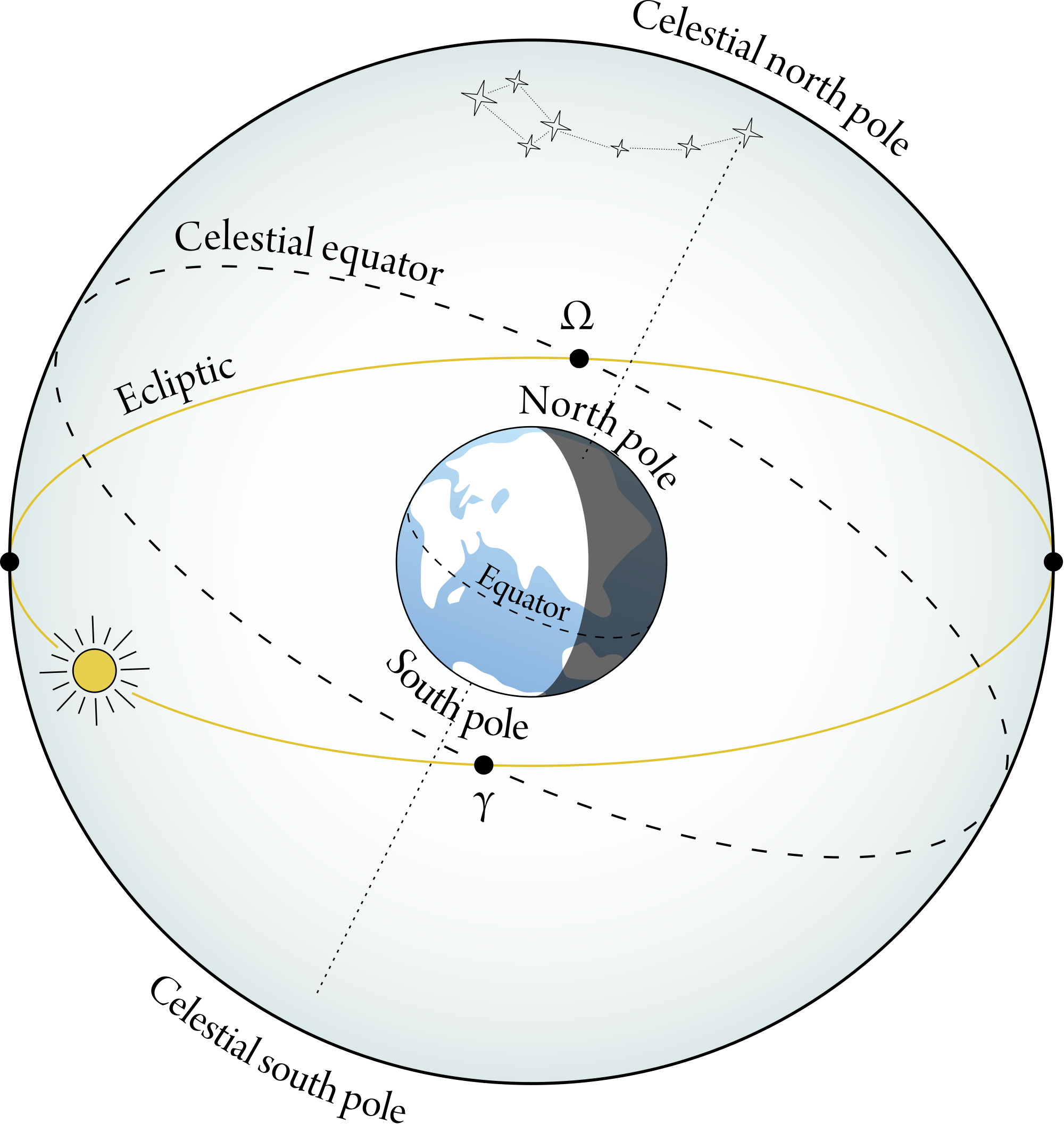
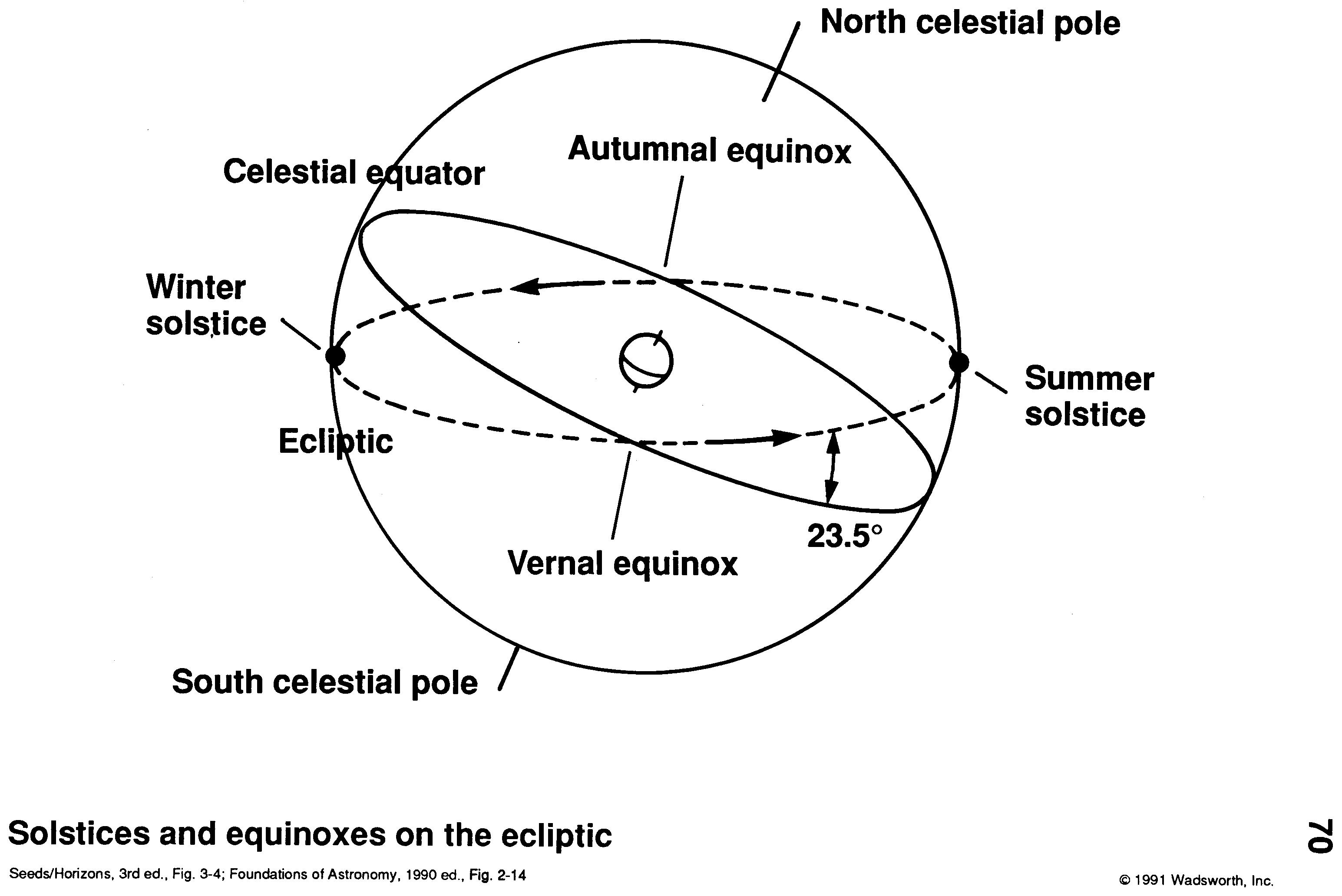
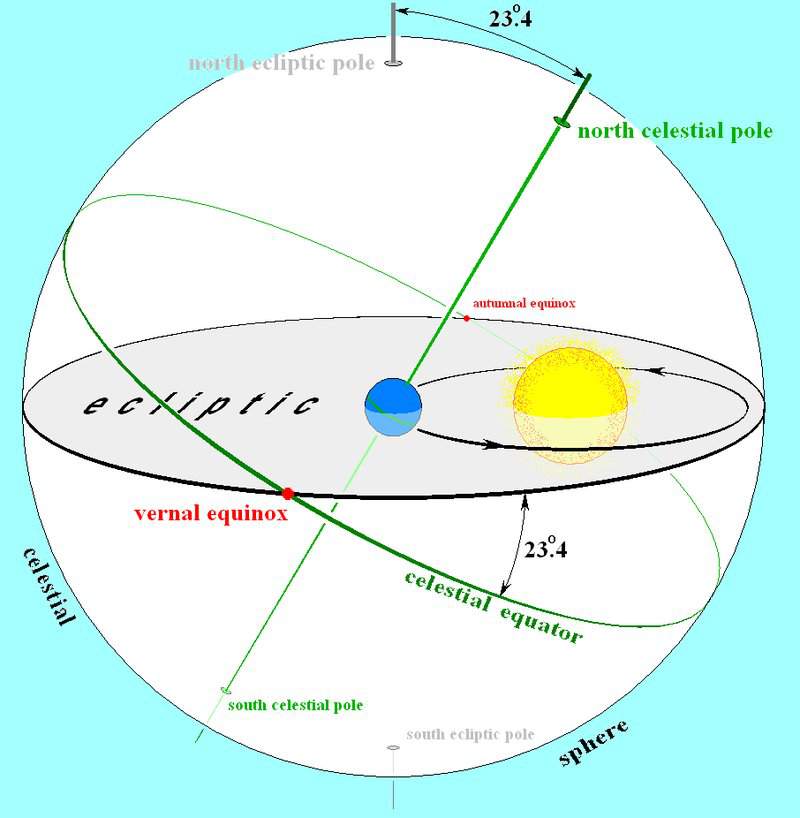
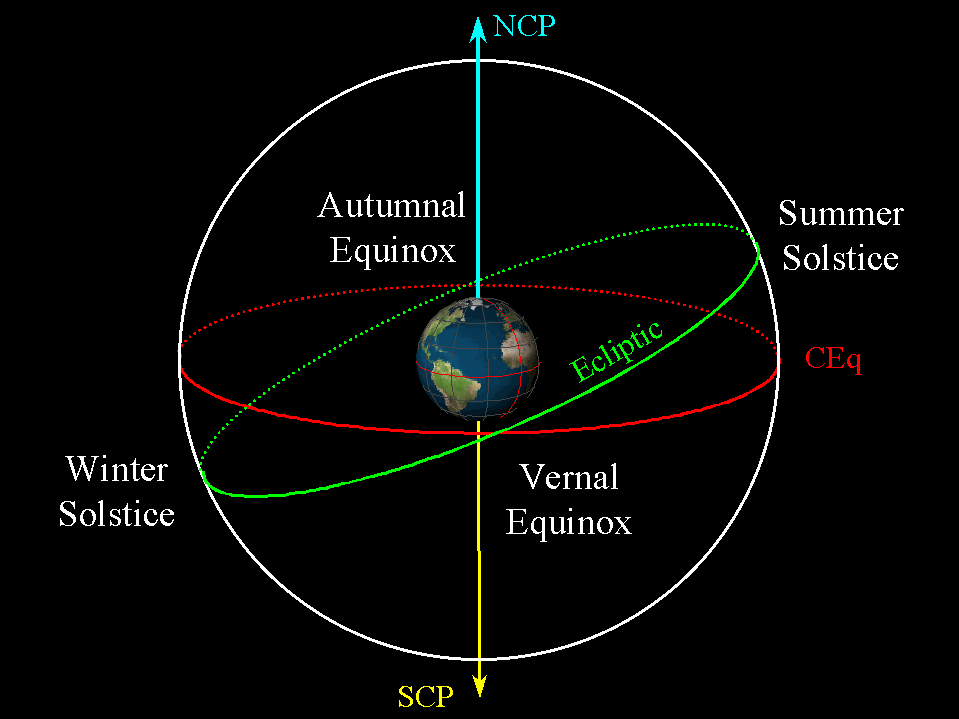
This great circle is called the ecliptic, and it is the projection of the plane of Earth's orbit on the celestial sphere. The angle between the ecliptic and the equator is called the Obliquity of the Ecliptic. The ecliptic crosses the equator at two points. The Sun reaches one of these points on about March 22 each year on its way north at.
About 'The obliquity of the ecliptic' Sherlock Role Play Amino
THE OBLIQUITY OF THE ECLIPTIC Ancient, mediaeval, and modern observations of the obliquity of the Ecliptic, measuring the inclination of the earth's axis, in ancient times and up to the present by George F. DodwellB.A., FRAS * *B.A. is Bachelor of Arts -- his degree was in mathematics (which was an art then).
About 'The obliquity of the ecliptic' Sherlock Role Play Amino
The ecliptic is inclined at 23.44° to the plane of the celestial equator; this inclination is called the obliquity of the ecliptic. The two points of intersection of the ecliptic and the plane mark the vernal and autumnal equinoxes.

Obliquity Arc [Wndsn Quadrant Telemeters]
obliquity of the ecliptic ( symbol ε) The angle between the Earth's equator and the ecliptic. It is the same as the Earth's axial tilt. The mean obliquity, corresponding to the mean equator, is currently just over 23° 26′, but is decreasing slowly at a rate of 47.5″ per century because of planetary perturbations of the Earth's orbit.
What is Obliquity A Celestial Body and Earths Axial Tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. [1] It differs from orbital inclination.
Celestial Mechanics III Time and reference frames Orbital
The angle of tilt is +23°26', which is called the obliquity of the ecliptic (symbol ε). Any two great circles intersect at two nodes. The node where the Sun crosses the equator from south to north (the ascending node) is called the vernal (or spring) equinox. The Sun passes through this point around March 21st each year.
Lecture 6 Daily & Annual Motions
A geographical map of the Triassic Period (after Cox, with slight abridgement). Shaded areas mark fossil sites. DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS Of the amphibians and reptiles of the Triassic Period, many species had large bodies with cumbersome movements and their fossils are distributed widely.
Ecliptic coordinates
Stellarium images around the March equinox and the June solstice, showing 30 degrees of ecliptic longitude and 2 hours of right ascension for comparison. Equatorial grid is blue, ecliptic grid is orange, ecliptic is yellow. The equation of time is the cumulative sum of differences between mean and apparent solar day length.

(a) The extreme case of the value of the orbit of the Moon to ecliptic
Obliquity of the ecliptic is the term used by astronomers for the inclination of Earth's equator with respect to the ecliptic, or of Earth's rotation axis to a perpendicular to the ecliptic.